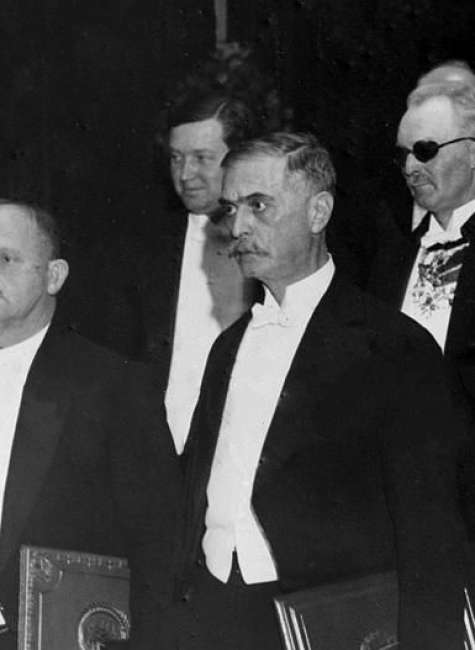
C. V. Raman (1888-1970)
The essence of science is independent thinking, hard work, and not equipment. When I got my Nobel Prize, I had spent hardly 200 rupees on my equipment.
Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman was an Indian physicist who made groundbreaking works in the field of light scattering. With his student K. S. Krishnan, he discovered that when light traverses a transparent material, some of the deflected light change wavelength and amplitude. This phenomenon was a new type of scattering of light and was subsequently known as the Raman effect Raman scattering. Raman won the 1930 Nobel Prize in Physics and was the first Asian person to receive a Nobel Prize in any branch of science.
Born to Hindu Tamil Brahmin parents, Raman was a precocious child, completing his secondary and higher secondary education from St Aloysius' Anglo-Indian High School at the ages of 11 and 13, respectively. He topped bachelor's degree examination at the University of Madras with honours in physics from Presidency College at age 16. His first research paper, on diffraction of light, was published in 1906 while still a graduate student. The next year he obtained an M.A. degree. He was 19 years of age when he joined the Indian Finance Service in Kolkata as Assistant Accountant General. There he became acquainted with the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science IACS, the first research institute in India, which allowed him to do independent research and where he made his major contributions in acoustics and optics.
In 1917, he was appointed as the first Palit Professor of Physics by Ashutosh Mukherjee at the Rajabazar Science College under the University of Calcutta. On his first trip to Europe, seeing the Mediterranean Sea motivated him to correctly describe the reason for the blue colour of the sea as a phenomenon of diffraction. He founded the Indian Journal of Physics in 1926. He and Krishnan discovered on 28 February 1928 a novel phenomenon of light scattering, which they called "modified scattering," but more famously known as the Raman effect. The day is celebrated by the Government of India as the National Science Day every year. Raman moved to the Indian Institute of Science in Bangalore in 1933 to become its first Indian Director. There he founded the Indian Academy of Sciences the same year. He established the Raman Research Institute in 1948 where he worked to his last days.
In 1954, the Government of India honoured him with the first Bharat Ratna along with politician C. Rajagopalachari and philosopher Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan, its highest civilian award. He later smashed the medallion in protest against Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru's policies on scientific research.
Early life and education
C. V. Raman was born in Tiruchirapalli, Madras Presidency now Trichy, Tamil Nadu, to Hindu Tamil parents, Chandrasekhara Ramanathan Iyer and Parvathi Ammal. He was the second of eight siblings. His father was a teacher at the local high school, and earned a modest income. He recalled: "I was born with a copper spoon in my mouth. At my birth my father was earning the magnificent salary of ten rupees per month!" In 1892, his family moved to Visakhapatnam then Vishakapatnam or Vizagapatam or Vizag in Andhra Pradesh as his father was appointed to the faculty of physics at Mrs A.V. Narasimha Rao College. There Raman studied at St Aloysius' Anglo-Indian High School. He passed matriculation at age 11 and the FA examination equivalent to today's Intermediate exam, PUCPDC and +2 with a scholarship at age 13.
In 1902, Raman joined Presidency College in Madras now Chennai where his father had been transferred to teach mathematics and physics. In 1904, he obtained a B.A. degree from the University of Madras, where he stood first and won the gold medal in physics. At age 18, while still a graduate student, he published his first scientific paper on diffraction of light in the British journal Philosophical Magazine in 1906. He completed an M.A. degree from the same university with highest distinction in 1907. His second paper published in the same journal that year was on surface tension of liquids. It was alongside Lord Rayleigh's paper on the sensitivity of ear to sound, and from which Lord Rayleigh started to communicate with Raman, courteously addressing him as "Professor."
Aware of Raman's capacity, his physics teacher Richard Llewellyn Jones insisted him to continue research in England. Jones arranged for Raman's physical inspection with Colonel Sir Gerald Giffard. The inspection revealed that Raman would not withstand the harsh weathers of England, the incident of which he later recalled, and said, " examined me and certified that I was going to die of tuberculosis… if I were to go to England."
Career
Raman's elder brother Chandrasekhara Subrahmanya Ayyar had joined the Indian Finance Service now Indian Audit and Accounts Service. In no condition to study abroad, Raman followed suit and qualified for the Indian Finance Service with first position in the entrance examination in February 1907. He later commented, "I took one look at all the candidates who had assembled there and I knew I was going to stand first." He was posted in Calcutta now Kolkata as Assistant Accountant General in June 1907. It was there that he became highly impressed with the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science IACS, the first research institute founded in India in 1876. He immediately befriended Asutosh Dey, who would eventually become his lifelong collaborators, Amrita Lal Sircar, founder and secretary of IACS, and Ashutosh Mukherjee, executive member of the institute and Vice Chancellor of the University of Calcutta. With such a connection, he obtained permission to conduct research in his own time. Up to that time the institute had not yet recruited regular researchers, or produced any research papers. Raman's article "Newton's rings in polarised light" was published in Nature in 1907 from the institute.
In 1909, Raman was transferred to Rangoon, Burma now Myanmar, to take up the position of currency officer. After only a few months, he had to return to Madras as his father succumbed to fatal illness. The subsequent death of his father and funeral rituals made him stay there for the rest of the year. Soon after he resumed office at Rangoon, he was transferred to Nagpur, Maharashtra in 1910. Even before he served for a year in Nagpur, he was promoted to Accountant General in 1911 and again posted to Calcutta.
From 1915, the University of Calcutta started assigning research scholars under Raman at IACS. Sudhangsu Kumar Banerji who later become Director General of Observatories of India Meteorological Department, a PhD scholar under Ganesh Prasad, was his first student. In 1917, the University of Calcutta instituted a new chair of physics named the Palit Professor of Physics, after the benefactor Sir Taraknath Palit. Ashutosh Mukherjee invited Jagadish Chandra Bose to take up the position, but Bose declined. As a second choice, Raman became the first Palit Professor of Physics and was posted to the newly formed Rajabazar Science College campus of the University of Calcutta. He reluctantly resigned as a civil servant after a decade of service, which was described as "supreme sacrifice" since his salary as a professor would be roughly half of his salary at the time. But the advantage was that he could delve into dedicated research, as explicitly indicated in the report of his joining the university, which stated:
Mr C.V. Raman’s acceptance of the Sir T N Palit Professorship on condition that he will not be required to go out of India... Reported that Mr C. V. Raman joined his appointment as Palit Professor of Physics from 2.7.17... Mr Raman informed that he will not be required to take any teaching work in MA and MSc classes, to the detriment of his own research or assisting advanced students in their researches.
The University of Calcutta allotted PhD students to Raman, and other universities followed suit including University of Allahabad, Rangoon University, Queen's College Indore, Institute of Science, Nagpur, Krisnath College, and University of Madras. By 1919, Raman had guided more than a dozen students. Following Sircar's death in 1919, Raman received two honorary positions at IACS, Honorary Professor and Honorary Secretary. He referred to this period as the "golden era" of his life.
Raman's appointment as the Palit Professor was strongly objected to by some members of the Senate of the University of Calcutta, especially foreign members, as Raman had no PhD and had never studied abroad. As a kind of rebuttal Mukherjee arranged for an honorary DSc which the University of Calcutta conferred Raman in 1921. The same year he visited Oxford to deliver a lecture at the Congress of Universities of the British Empire. He was by then widely known, and his hosts were J. J. Thomson and Lord Rutherford. Upon his election as Fellow of the Royal Society in 1924, Mukherjee asked him of his future plans, he replied, "The Nobel Prize of course." In 1926, he established the Indian Journal of Physics as the first editor. The second volume of the journal published his famous article "A new radiation", reporting the discovery of the Raman effect.
Raman was succeeded by Debendra Mohan Bose as the Palit Professor in 1932. In 1933, he left Kolkata to join the Indian Institute of Science in Bangalore as its first Indian director. Maharaja Krishnaraja Wadiyar IV, the King of Mysore, Jamsetji Tata and Nawab Sir Mir Osman Ali Khan, the Nizam of Hyderabad, had contributed the lands and funds for the Indian Institute of Science in Bangalore. The Viceroy of India, Lord Minto approved the establishment in 1909, and the British government appointed its first Director, Morris Travers. Raman was the fourth Director. During his tenure at IISc, he recruited G. N. Ramachandran, who later went on to become a distinguished X-ray crystallographer. He founded the Indian Academy of Sciences in 1934 and started publishing the proceedings of the academy.
With his former student Panchapakesa Krishnamurti, Raman started a company called Travancore Chemical and Manufacturing Co. Ltd. in 1943. The company, renamed as TCM Limited in 1996, was one of the first organic and inorganic chemical manufacturers. In 1947, Raman was appointed as the first National Professor by the new government of Independent India.
Raman retired from the Indian Institute of Science in 1948 and established the Raman Research Institute in Bangalore a year later. He served as its director and remained active there until his death in 1970.
Scientific contributions
Musical sound
One of Raman's interests was understanding the physics of musical sounds. He was inspired by Hermann von Helmholtz’s The Sensations of Tone, the book he came across when he joined IACS. He studied and published his findings quite prolifically between 1916 and 1921. He worked out the theory of transverse vibration of bowed string instruments, on the basis of superposition of velocities. One of his earliest studies was on the wolf tone in violins and cellos. He studied the acoustics of various violin and related instruments, including Indian stringed instruments, and water splashes. He even performed "Experiments with mechanically-played violins."

Raman also studied the uniqueness of Indian drums. His analyses of the harmonic nature of the sound of tabla and mridangam were the first scientific studies on Indian percussion. He wrote a critical research on Kaufmann's theory on vibrations of the pianoforte string. During his brief visit of England in 1921, he managed to study how sound travels in the Whispering Gallery of the dome of St Paul's Cathedral in London that produces unusual sound effects. His work on acoustics was an important prelude, both experimentally and conceptually, to his later works on optics and quantum mechanics.
Blue colour of the sea
Raman, in his broadening venture on optics, started to investigate scattering of light starting in 1919. His first phenomenal discovery was the physics of the blue colour of seawater. During a voyage home from England on board the S.S. Narkunda in September 1921, he contemplated the blue colour of the Mediterranean Sea. Using simple optical equipment, a pocket-sized spectroscope and a Nicol prism in hand, he studied the seawater. Of several hypotheses on the colour of the sea, the best explanation had been that of Lord Rayleigh's in 1910, according to which "The much admired dark blue of the deep sea has nothing to do with the colour of water, but is simply the blue of the sky seen by reflection". Rayleigh had correctly described the nature of the blue sky by a phenomenon now known as Rayleigh scattering, the scattering of light and refraction by particles in the atmosphere. The Nicol prism allowed Raman to view the water without the influence of sunlight reflected by the surface. He described how the sea appears even more blue than usual, contradicting Rayleigh.
As soon as the S.S. Narkunda docked in Bombay Harbour, Raman finished an article "The colour of the sea" published in the November 1921 issue of Nature. He noted that Rayleigh's explanation is "questionable by a simple mode of observation" using his prism. When he reached Calcutta, he asked his student K.R. Ramanathan who was from the University of Rangoon to conduct research at IACS. By early 1922, Raman stated:
Looking down into the water with a Nicol in front of the eye to cut off surface reflections, the track of the sun’s rays could be seen entering the water and appearing by virtue of perspective to converge to a point at a considerable depth inside it. The question is: What is it that diffracts the light and makes its passage visible? An interesting possibility that should be considered in this connection is that the diffracting particles may, at least in part, be the molecules of the water themselves.
True to his words, Ramanathan published an elaborate experimental finding in 1923. The subsequent study in the Bay of Bengal in 1924 provided the full evidence.
Raman effect
Background
Raman's second important discovery on the scattering of light was a new type of radiation, an eponymous phenomenon called Raman effect. In 1925, K. S. Krishnan, the Research Associate in his laboratory, noted the theoretical background for the existence of an additional scattering line beside the usual polarised elastic scattering when light scatters through liquid. But the theoretical attempts to justify the phenomenon were quite futile for the next 2 years. The major impetus was the discovery of Compton effect. Arthur Compton at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology had found evidence in 1923 that electromagnetic waves can also be described as particles. By 1927, the phenomenon was widely accepted by scientists, including Raman. As the news of Compton's Nobel Prize in Physics was announced in December 1927, Raman ecstatically told Krishnan, saying:
"Excellent news... very nice indeed. But look here Krishnan. If this is true of X-Rays, it must be true of Light too. I have always thought so. There must be an Optical analogue to Compton Effect. We must pursue it and we are on the right lines. It must and shall be found. The Nobel Prize must be won."
But the origin of the inspiration went further. As Compton later recollected "that it was probably the Toronto debate that led him to discover the Raman effect two years later." The Toronto debate was about the discussion on the existence of light quantum at the British Association for the Advancement of Science meeting held at Toronto in 1924. There Compton presented his experimental findings, which William Duane argued with his own with evidence that light was a wave. Raman took Duane's side and said, "Compton, you're a very good debater, but the truth isn't in you."
The scattering experiments
Krishnan started the experiment at the beginning of January 1928. On 7 January Krishnan discovered that no matter what kind of pure liquid he used, it always produced polarised fluorescence within the visible spectrum of light. As Raman saw the result, he was astonished why he never observed such phenomenon all those years. That night they named the new phenomenon as "modified scattering" with reference to the Compton effect as unmodified scattering. On 16 February they sent a manuscript to Nature titled "A new type of secondary radiation", which was published on 31 March.
On 28 February 1928, Raman and Krishnan obtained spectra of the modified scattering separate from the incident light. Due to difficulty in measuring wavelengths of light, they had been relying on visual observation of the colour produced from sunlight through prism. Raman had invented an instrument for detecting and measuring electromagnetic waves called a spectrograph. That moment they could employ the instrument using monochromatic light from a mercury arc lamp which penetrated transparent material and was allowed to fall on a spectrograph to record its spectrum. The lines of scattering could now be measured and photographed.
Announcement
The same day, Raman made the announcement to the press. The Associated Press of India reported it the next day, on 29 February, as "New theory of radiation: Prof. Raman's Discovery." It ran the story as:
Prof. C. V. Raman, F.R.S., of the Calcutta University, has made a discovery which promises to be of fundamental significance to physics... The new phenomenon exhibits features even more startling than those discovered by Prof. Compton with X-rays. The principal feature observed is that when matter is excited by light of one colour, the atoms contained in it emit light of two colours, one of which is different from the exciting colour and is lower down the spectrum. The astonishing thing is that the altered colour is quite independent of the nature of the substance used.
The news was reproduced by The Statesman on 1 March under the headline "Scattering of Light by Atoms – New Phenomenon – Calcutta Professor's Discovery." Raman submitted a three-paragraph report of the discovery on 8 March to Nature and was published on 21 April. The actual data was sent to the same journal on 22 March and was published on 5 May. Raman presented the formal and detail description as "A new radiation" at the meeting of South Indian Science Association in Bangalore on 16 March. His lecture was published in the Indian Journal of Physics on 31 March. 1,000 copies of the paper reprint was sent to scientists in different countries on that day.
Reception and outcome
Some physicists, particularly French and German physicists were initially sceptical of the authenticity of the discovery. Georg Joos at the Friedrich Schiller University of Jena asked Arnold Sommerfeld at the University of Munich, "Do you think that Raman's work on the optical Compton effect in liquids is reliable?... The sharpness of the scattered lines in liquids seems doubtful to me". Sommerfield tried to reproduce the experiment, but failed. On 20 June, Peter Pringsheim at the University of Berlin was able to reproduce Raman's results successfully. He was the first to coin the terms Ramaneffekt and Linien des Ramaneffekts in his articles published the following months. Use of the English versions, "Raman effect" and "Raman lines" immediately followed.
In addition to being a new phenomenon itself, the Raman effect was one of the earliest proofs of the quantum nature of light. Robert W. Wood at the Johns Hopkins University was the first American to confirm the Raman effect in the early 1929. He made a series of experimental verification, after which he commented, saying, "It appears to me that this very beautiful discovery which resulted from Raman's long and patient study of the phenomenon of light scattering is one of the most convincing proofs of the quantum theory". The field of Raman spectroscopy came to be based on this phenomenon, and Ernest Rutherford, President of the Royal Society, referred to it in his presentation of the Hughes Medal to Raman in 1930 as "among the best three or four discoveries in experimental physics in the last decade".
Raman was confident that he would win the Nobel Prize in Physics as well but was disappointed when the Nobel Prize went to Owen Richardson in 1928 and to Louis de Broglie in 1929. He was so confident of winning the prize in 1930 that he booked tickets in July, even though the awards were to be announced in November. He would scan each day's newspaper for announcement of the prize, tossing it away if it did not carry the news. He did eventually win it in 1930.
Later work
Raman and Suri Bhagavantam determined the spin of photons in 1932, which further confirmed the quantum nature of light.
Raman had association with the Banaras Hindu University in Varanasi. He attended the foundation ceremony of BHU and delivered lectures on mathematics and "Some new paths in physics" during the lecture series organised at the university from 5 to 8 February 1916. He also held the position of permanent visiting professor at BHU.
Raman and his student, Nagendra Nath, provided the correct theoretical explanation for the acousto-optic effect light scattering by sound waves, in a series of articles resulting in the celebrated Raman–Nath theory. Modulators, and switching systems based on this effect have enabled optical communication components based on laser systems.
Other investigations carried out by Raman were experimental and theoretical studies on the diffraction of light by acoustic waves of ultrasonic and hypersonic frequencies published 1934–1942, and those on the effects produced by X-rays on infrared vibrations in crystals exposed to ordinary light.
In 1948, Raman, through studying the spectroscopic behaviour of crystals, approached in a new manner fundamental problems of crystal dynamics. He dealt with the structure and properties of diamond, the structure and optical behaviour of numerous iridescent substances including labradorite, pearly feldspar, agate, opal, and pearls. Among his other interests were the optics of colloids, electrical and magnetic anisotropy, and the physiology of human vision.
Personal life
Raman married Lokasundari Ammal 1892–1980 on 6 May 1907. It was a self-arranged marriage and his wife was 13 years old. His wife later recounted apparently jokingly that their marriage was not so much about her musical prowess she was playing veena when they first met as "the extra allowance which the Finance Department gave to its married officers." Married officers got additional INR 150. Soon after they moved to Calcutta in 1907, the couple were accused of converting to Christianity. It was because they were fascinated by St. John's Church, Kolkata and often visited it, Lokasundari for the music and Raman for the acoustics.
They had two sons, Chandrasekhar Raman and radio-astronomer Venkatraman Radhakrishnan. Raman was the paternal uncle of Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar, recipient of the 1983 Nobel Prize in Physics.
Throughout his life, Raman developed an extensive personal collection of stones, minerals, and materials with interesting light-scattering properties, which he obtained from his world travels and as gifts. He often carried a small, handheld spectroscope to study specimens. These are on display at the Raman Research Institute, where he worked and taught.
Lord Rutherford was instrumental in some of Raman's most pivotal moments in life. He nominated Raman for the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930, presented him the Hughes Medal as President of the Royal Society in 1930, and recommended him for the position of Director at IISc in 1932.
Raman had a sense of obsession with the Nobel Prize. In a speech at the University of Calcutta, he said, "I'm not flattered by the honour done to me. This is a small achievement. If there is anything that I aspire for, it is the Nobel Prize. You will find that I get that in five years." Soon after he received the Nobel Prize, he was asked in an interview the possible consequences if he had discovered the Raman effect earlier, which he replied, "Then I should have shared the Nobel Prize with Compton and I should not have liked that; I would rather receive the whole of it."
Religious views
Although Raman hardly talked about religion, he was openly an agnostic, but objected to being labeled atheist. He however did not give up Hindu traditional rituals. Traditional pagri Indian turban with a tuft underneath and a upanayana Hindu sacred thread were his signature attire. Though it was not customary to wear turbans in South Indian culture, he explained his habit as, "Oh, if I did not wear one, my head will swell. You all praise me so much and I need a turban to contain my ego." He even attributed his turban for the recognition he received on his first visit to England, particular from J. J. Thomson and Lord Rutherford. In a public speech, he once said,
There is no Heaven, no Swarga, no Hell, no rebirth, no reincarnation and no immortality. The only thing that is true is that a man is born, he lives and he dies. Therefore, he should live his life properly.
In a friendly meeting with Mahatma Gandhi and Gilbert Rahm, a German zoologist, the conversation turned to religion. Raman spoke,
Death
At the end of October 1970, Raman had a cardiac arrest and collapsed in his laboratory. He was moved to the hospital where the doctors diagnosed his condition and declared that Raman would not live more than four hours. He however survived a few days and requested to stay in the gardens of his institute surrounded by his followers.
Two days before Raman died, he told one of his former students, "Do not allow the journals of the Academy to die, for they are the sensitive indicators of the quality of science being done in the country and whether science is taking root in it or not." That evening, Raman met with the Board of Management of his institute and discussed from his bed with them any proceedings of the institute's management. He also willed his wife to perform a simple cremation without any rituals upon his death. He died from natural causes early the next morning on 21 November 1970 at the age of 82.
On the news of Raman's death, Prime Minister Indira Gandhi publicly announced, saying,
The country, the House [of Parliament], and everyone of us will mourn the death of Dr. C. V. Raman. He was the greatest scientist of modern India and one of the greatest intellects our country has produced in its long history. His mind was like the diamond, which he studied and explained. His life's work consisted in throwing light upon the nature of lights, and the world honoured him in many ways for the new knowledge which he won for science.
Controversies
The Nobel Prize
Independent discovery
In 1928, Grigory Landsberg and Leonid Mandelstam at the Moscow State University independently discovered the Raman effect. They published their findings in July issue of Naturwissenschaften, and presented their findings at the Sixth Congress of the Russian Association of Physicists held at Saratov from 5 to 16 August. In 1930, they were nominated for the Nobel Prize alongside Raman. According to the Nobel Committee, however: 1 the Russians did not come to an independent interpretation of their discovery as they cited Raman's article; 2 they observed the effect only in crystals, whereas Raman and Krishnan observed it in solids, liquids and gases, and therefore proved the universal nature of the effect; 3 the problems concerning the intensity of Raman and infrared lines in the spectra had been explained during the previous year; 4 the Raman method had been applied with great success in different fields of molecular physics; and 5 the Raman effect had effectively helped to check the symmetry properties of molecules, and thus the problems concerning nuclear spin in atomic physics.
The Nobel Committee proposed only Raman's name to the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences for the Nobel Prize. Evidence later appeared that the Russians had discovered the phenomenon earlier, a week before Raman and Krishnan's discovery. According to Mandelstam's letter to Orest Khvolson, the Russian had observed the spectral line on 21 February 1928.
Role of Krishnan
Krishnan was not nominated for the Nobel Prize even though he was the main researcher in the discovery of Raman effect. It was he alone who first noted the new scattering. Krishnan co-authored all the scientific papers on the discovery in 1928 except two. He alone wrote all the follow-up studies. Krishnan himself never claimed himself worthy of the prize. But Raman admitted later that Krishnan was the co-discoverer. He however remained openly antagonistic towards Krishnan, which Krishnan described as "the greatest tragedy of my life." After Krishnan's death, Raman said to a correspondent from The Times of India, "Krishnan was the greatest charlatan I have known, and all his life he masqueraded in the cloak of another man's discovery."
The Raman–Born controversy
During October 1933 – March 1934, Max Born was employed by IISc as a Reader in Theoretical Physics following the invitation by Raman early in 1933. Born at the time was a refugee from Nazi Germany and temporarily employed at St John's College, Cambridge. Since the beginning of the 20th century Born had developed a theory on lattice dynamics based on thermal properties. He presented his theory in one his lectures at IISc. By then Raman had developed a different theory and claimed that Born's theory contradicted the experimental data. Their debate lasted for decades.
In this dispute, Born received support from most physicists, as his was proven to a better explanation. Raman's theory was generally regarded as having a partial relevance. Beyond the intellectual debate, their rivalry extended to personal and social levels. Born later referred to Raman as his "enemy." In spite of the mounting evidence for Born's theory, Raman refused to concede. He even rejected articles submitted to Current Science as the editor which supported Born's theory. Born was nominated several times for the Nobel Prize specifically for his contributions to lattice theory, and eventually won it for his statistical works on quantum mechanics in 1954. The account was written as a "belated Nobel Prize."
Indian authorities
Raman had an aversion to the then Prime Minister of India Jawaharlal Nehru and Nehru's policies on science. In one instance he smashed the bust of Nehru on the floor. In another he shattered to pieces with a hammer his Bharat Ratna medallion, as it was given to him by the Nehru government. He publicly ridiculed Nehru when the latter visited the Raman Research Institute in 1948. They displayed a piece of gold and copper against an ultraviolet light. Nehru was tricked into believing that copper which glowed more brilliantly than any other metal was gold. Raman was quick to remark, "Mr Prime Minister, everything that glitters is not gold."
On the same occasion Nehru, offered Raman financial assistance to his institute which Raman flatly refused by replying, "I certainly don't want this to become another government laboratory." Raman was particularly against the control of research programmes by the government such as the establishment of the Bhabha Atomic Research Centre BARC, Defense Research and Development Organization DRDO, and the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research CSIR. He remained hostile to people associated with these establishments such as Homi J. Bhabha, S.S. Bhatnagar, and his once favourite student, Krishnan. He even called such programmes as the "Nehru–Bhatnagar effect." In 1959, Raman proposed to establish another research institute in Madras. The Government of Madras advised him to apply for funds from the central government. But Raman clearly foresaw, as he replied to C. Subramaniam then the Minister for Finance Education in Madras, that his proposal to Nehru's government "would be met with a refusal." So ended the plan.
Raman described AICC authorities as "a big tamasha" drama or spectacle that just kept on discussing issues without action. As to problems of food resources in India, his advice to the government was, "We must stop breeding like pigs and the matter will solve itself."
Indian Academy of Sciences
The Indian Academy of Sciences was born out of conflicts during the procedures of proposal for a national scientific organisation in line with the Royal Society. In 1933, the Indian Science Congress Association ISCA, at the time the largest scientific organisation, planned to establish a national science body, which would be authorised to advice the government on scientific matters. Sir Richard Gregory, then editor of Nature on his visit to India, had suggested Raman, as editor of Current Science, to establish an Indian Academy of Sciences. Raman was of the opinion that it should be an exclusively Indian membership as opposed to the general consensus that British members should be included. He resolved that "How can India Science prosper under the tutelage of an academy which has its own council of 30, 15 of who are Britishers of whom only two or three are fit enough to be its Fellows." On 1 April 1933 he convened a separate meeting of the south Indian scientists. He and Subba Rao officially resigned from ISCA.
Raman registered the new organisation as Indian Academy of Sciences on 24 April to the Registrar of Societies. It was a provisional name to be changed to the Royal Society of India after approval from the Royal Charter. The Government of India did not recognise it as an official national scientific body, as such the ICSA created a separate organisation named the National Institute of Sciences of India on 7 January 1935 but again changed to the Indian National Science Academy in 1970. INSA had been led by the foremost rivals of Raman including Meghnad Saha, Bhabha, Bhatnagar, and Krishan.
Indian Institute of Science
Raman had a great fallout with the authorities at the Indian Institute of Science IISc. He was accused of biased development in physics, while ignoring other fields. He lacked diplomatic personality on other colleagues, which S. Ramaseshan, his nephew and later Director of IISc, reminisced, saying, "Raman went in there like a bull in a china shop." He wanted research in physics at the level of those of western institutes, but at the expense of other fields of science. Max Born observed, "Raman found a sleepy place where very little work was being done by a number of extremely well paid people." At the Council meeting Kenneth Aston, professor in the Electrical Technology Department, harshly criticised Raman and Raman's recruitment of Born. Raman had every intention of giving full position of professor to Born. Aston even made personal attack on Born by referring to him as someone "who was rejected by his own country, a renegade and therefore a second-rate scientist unfit to be part of the faculty, much less to be the head of the department of physics."
The Council of IISc constituted a review committee to oversee Raman's conduct in January 1936. The committee, chaired by James Irvine, Principal and Vice Chancellor of the University of St Andrews, reported in March that Raman had misused the funds and entirely shifted the "centre of gravity" in research to physics, and also that the proposal of Born as Professor of Mathematical Physics which was already approved by the Council in November 1935 was not financially feasible. The Council offered Raman two choices, either to resign from the institute with effect from 1 April or resign as the Director and continue as Professor of physics. If he did not make the choice, he was to be fired. Raman was compelled to make the second choice.
The Royal Society
Raman never seemed to have thought highly of the Fellowship of the Royal Society. He tendered his resignation as a Fellow on 9 March 1968, which the Council of the Royal Society accepted on 4 April. However, the exact reason was not documented. One reason could be Raman's objection to the designation "British subjects" as one of the categories of the Fellows. Particularly after the Independence of India, the Royal Society had its own disputes on this matter.
According to Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar, The London Times had once made a list of the Fellows, in which Raman was omitted. Raman wrote to and demanded Patrick Blackett, the then President of the society, for an explanation. He was dejected by Blackett's response that the society had no role in the newspaper. According to Krishnan, it was because of a disapproving review Raman received on a manuscript he had submitted to the Proceedings of the Royal Society. It could have been these cumulative factors as Raman wrote in his resignation letter, and said, "I have taken this decision after careful consideration of all the circumstances of the case. I would request that my resignation be accepted and my name removed from the list of the Fellows of the Society."
Honours and awards
Raman was honoured with many honorary doctorates and memberships of scientific societies. He was member of the Deutsche Akademie of Munich, Swiss Physical Society of Zürich, Royal Philosophical Society of Glasgow, Royal Irish Academy, Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Academy of Sciences of the U.S.S.R., Optical Society of America and Mineralogical Society of America, Romanian Academy of Sciences, Catgut Acoustical Society of America, and Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences.
In 1924, he was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society. However, he resigned from the fellowship in 1968 for unrecorded reasons, the only Indian FRS ever to do so.
He was the President of the 16th session of the Indian Science Congress in 1929. He was the founder President of the Indian Academy of Sciences from 1933 till his death. He was member of the Pontifical Academy of Sciences in 1961.
Awards
- In 1912, Raman received the Curzon Research Award, while still working in the Indian Finance Service.
- In 1913, he received the Woodburn Research Medal, while still working in the Indian Finance Service.
- In 1928, he received the Matteucci Medal from the Accademia Nazionale delle Scienze in Rome.
- In 1930, he was knighted. An approval for his inclusion in the 1929 Birthday Honours was delayed, and Lord Irwin, the Viceroy of India, conferred him Knight Bachelor in a special ceremony at the Viceroy's House now Rashtrapati Bhawan in New Delhi.
- In 1930, he won the Nobel Prize in Physics "for his work on the scattering of light and for the discovery of the effect named after him." He was the first Asian and first non-white to receive any Nobel Prize in the sciences. Before him, Rabindranath Tagore also Indian had received the Nobel Prize for Literature in 1913.
- In 1930, he received the Hughes Medal of the Royal Society.
- In 1941, he was awarded the Franklin Medal by the Franklin Institute in Philadelphia.
- In 1954, he was awarded the Bharat Ratna.
- In 1957, he was awarded the Lenin Peace Prize.
Posthumous recognition and contemporary references
- India celebrates National Science Day on 28 February of every year to commemorate the discovery of the Raman effect in 1928.
- Postal stamps featuring Raman were issued in 1971 and 2009.
- A road in India's capital, New Delhi, is named C. V. Raman Marg.
- An area in eastern Bangalore is called CV Raman Nagar.
- The road running north of the national seminar complex in Bangalore is named C. V. Raman Road.
- A building at the Indian Institute of Science in Bangalore is named the Raman Building.
- A hospital in eastern Bangalore on 80 Ft. Rd. is named the Sir C. V. Raman Hospital.
- There is also CV Raman Nagar in Trichy, his birthplace.
- Raman, a lunar crater is named after C. V. Raman.
- C. V. Raman Global University was established in 1997.
- In 1998, the American Chemical Society and Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science recognised Raman's discovery as an International Historic Chemical Landmark at the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science in Jadavpur, Calcutta, India. The inscription on the commemoration plaque reads:At this institute, Sir C. V. Raman discovered in 1928 that when a beam of coloured light entered a liquid, a fraction of the light scattered by that liquid was of a different color. Raman showed that the nature of this scattered light was dependent on the type of sample present. Other scientists quickly understood the significance of this phenomenon as an analytical and research tool and called it the Raman Effect. This method became even more valuable with the advent of modern computers and lasers. Its current uses range from the non-destructive identification of minerals to the early detection of life-threatening diseases. For his discovery Raman was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930.
- Dr. C.V. Raman University was established in Chhattisgarh in 2006.
- On 7 November 2013, a Google Doodle honoured Raman on the 125th anniversary of his birthday.
- Raman Science Centre in Nagpur is named after Sir C. V. Raman.
- Dr. C.V. Raman University, Bihar was established in 2018.
- Dr. C.V. Raman University, Khandwa was established in 2018.
More facts
Matteucci Medal (1928)
Knight Bachelor (1930)
Hughes Medal (1930)
Nobel Prize in Physics (1930)
Bharat Ratna (1954)
Lenin Peace Prize (1957)
Beyond Rainbows: The Quest & Achievement of Dr. C.V. Raman (2004)
The Quantum Indians (2013)